What is Telematics Control Unit?
Nowadays, we hear about the term ‘Telematics’ a lot. What is it? It comprises of two words – Tele for Telecommunications & Matics for Informatics (Data). Telematics is the merging of telecommunications and informatics to send and receive data. It is a method of capturing and processing the driving data. Manufacturers offer Telematics mainly in high-end vehicles for driver assistance, safety, and comfort. However, it will be a standard feature in most vehicles in the future. A Telematics Control Unit or TCU is the one that controls, connects, and manages telematics services in a modern car.
How Telematics Control Unit Works?
A telematics control unit (TCU) in automobiles is an embedded system fitted in vehicles for availing telematics services. Basically, it is a micro-controller (a complete computer on a single electronic chip). The TCU wirelessly connects the vehicle to cloud services or other vehicles via V2X standards over a mobile network. In addition, the TCU collects telemetry data from the car. The system connects & communicates with various sub-systems over data and control busses (CAN) in the vehicle and collects the telemetry data. This data includes elements such as position, speed, engine data, connectivity quality, etc. It may also provide in-vehicle connectivity thru’ Wifi and Bluetooth and enables the e-Call function on relevant markets.
Functions of Telematics Control Unit:
- Collect vehicle data thru’ CAN-BUS port
- Manage information collected over various communication interfaces
- Management of memory and battery
- Manage two-way communication with Telematics cloud server
- Manage communication with the user dashboard/HMI device
A TCU consists of the following components:
- A Satellite navigation (GNSS) unit to keep track of the latitude and longitude values of the vehicle.
- An external interface for mobile communication (GSM, GPRS, Wi-Fi, WiMax, LTE or 5G). It provides the tracked values to a centralized geographical information system (GIS) database server.
- An electronic processing unit.
- A microcontroller or a microprocessor or field programmable gate array (FPGA) to process the information and acts on the interface between the GPS.
- A mobile communication unit.
- Memory to retain GPS values in case of mobile-free zones or to intelligently store information about the vehicle’s sensor data.
- Battery module
- Bluetooth module
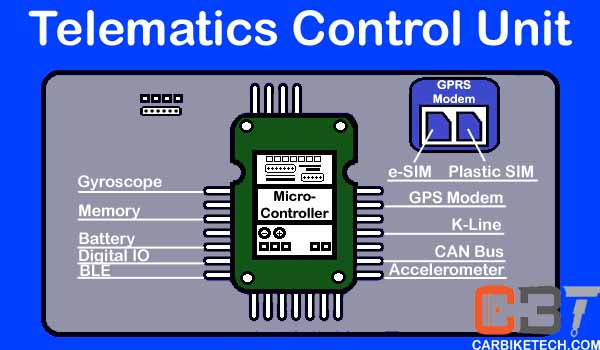
The micro-controller consists of:
- A gyroscope sensor for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity
- A GPS/GPRS modem
- A CAN bus
- An accelerometer
Software components:
- Boot loader
- Data storage module
- Data analytics module
- Power and battery management module
- Cloud communication module
- Data collection module
- Security module
- Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA)
- Device driver
- Custom application
Components of front end:
- User Interface (UI)
- Front end programming language
- Mark up
- Templates and
- CMS Web frameworks
Responsibilities of Telematics Control Unit:
1, Decapsulate telematics data as it passes on through web and application servers
2. Execute database queries and store data into the database
3. Responsibilities of telematics applications:
4. Enable user to view & access telematics data thru’ a mobile/web app
5. Integrate telematics data into 3rd party systems to improve brand & customer experience
Ficosa, LG, and Harman are some of the popular telematics control unit manufacturers in the world.
Watch How Telematics Control Unit System Works Here:
Read more: How Engine Management System Works?>>
