Engine Management System (EMS):
EMS stands for Engine Management System, consisting of a wide range of electronic and electrical components such as sensors, relays, actuators, and an Engine Control Unit. They work together to provide the Engine Management System with vital data parameters. These are essential for governing various engine functions effectively. Furthermore, modern-day engine technologies incorporate the EMS. These include MPFi & GDi systems in Petrol engines and CRDi systems in diesel engines for improved performance.
Engine Management System: What is ECU/ECM?
ECU stands for Engine Control Unit and ECM for Engine Control Module. Both are the same. However, it is also a generic term for any Electronic Control Unit/Module.
Engine Control Unit:
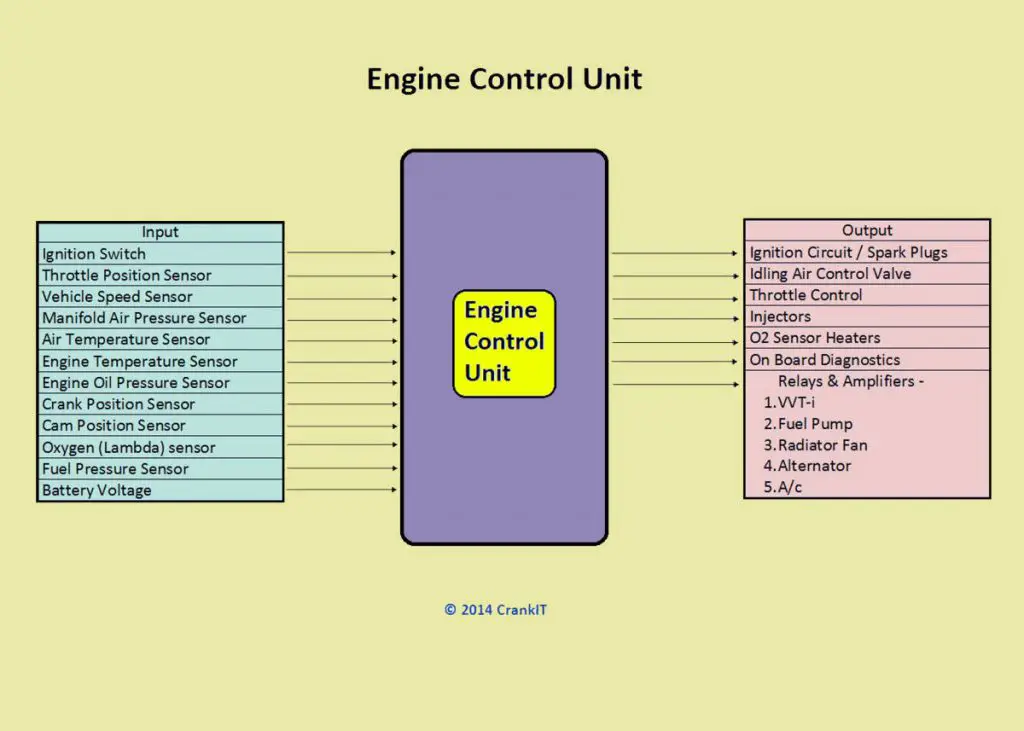
The Engine Control Unit is a central part of the Engine Management System, virtually the ‘Brain’ of the engine. It plays a vital role in collecting, analyzing, processing, and executing the data it receives from various sub-systems. Furthermore, an ECU comprises a computer that uses a microchip to process the inputs from multiple engine sensors in real-time.
Furthermore, the Electronic Control Unit contains hardware and software. The ECU’s printed circuit board (PCB) consists of a micro-controller chip or the CPU (Central Processing Unit). The micro-controller or chips on the PCB store the software. It is possible to re-program the ECU by updating the software or replacing chips. All the engine sensors send data inputs through electrical signals to the ECU. In turn, the ECU controls various actuators, ignition timing, variable valve timing, etc.
How an ECU Works?
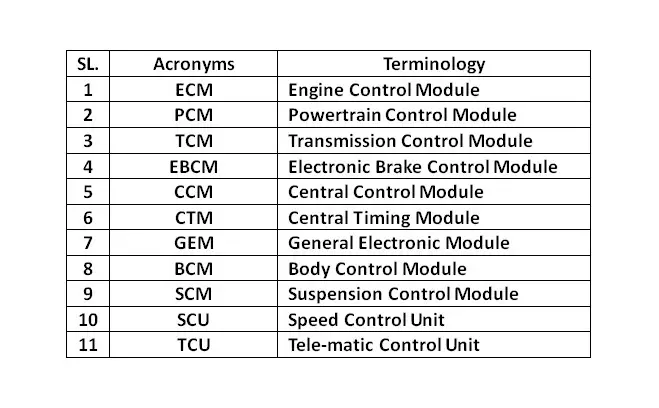
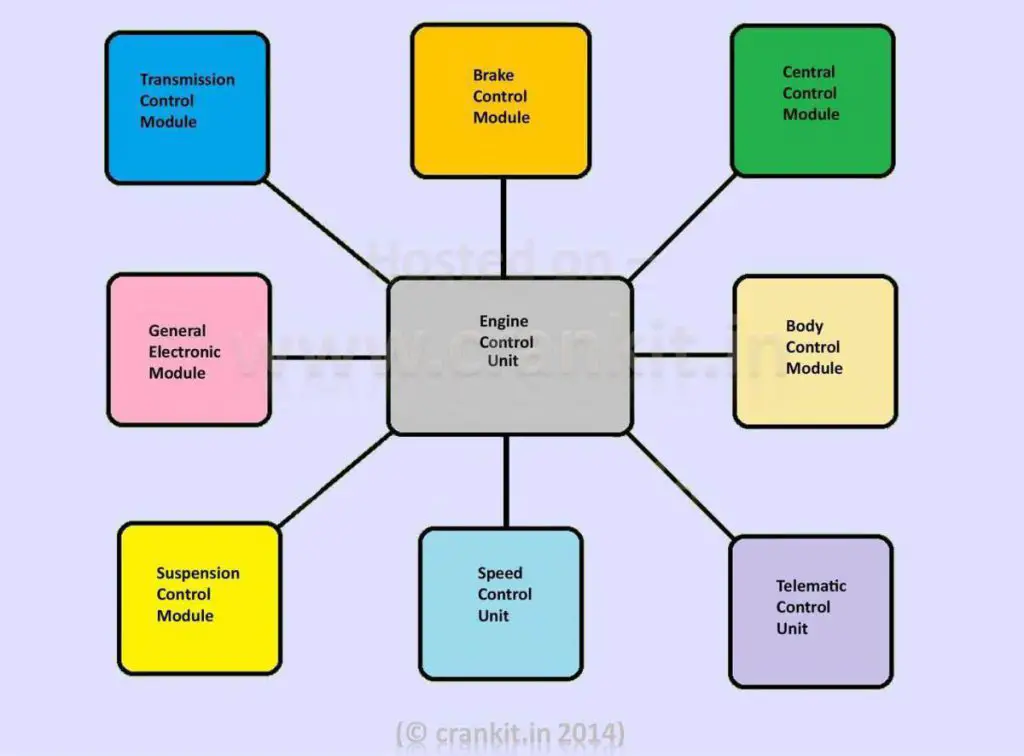
Based on this data input, the ECU precisely calculates and delivers the ideal air-fuel mixture. It also regulates the engine’s idle speed and limits the top speed of a vehicle. This system is also widely referred to as an ”Electronic Engine Management System” or the EMS. Furthermore, it is possible to customize the modern-day ECUs to suit different vehicular applications and varying customer demands. Also, some cars have an individual’ ‘Control Module” for all major systems. For example, a modern car has the following individual Control Modules that control the respective systems.
An Engine Control Unit connects to all the individual Electronic Control Modules (ECMs). A modern-day car consists of more than one Control Modules, each exclusive for every primary system, which improves performance. However, the manufacturers seldom refer to these systems as car computers since they are multiple computers instead of one.
Bosch, Delphi, and Hitachi are some of the world’s leading Engine Management System manufacturers.
Read more: Which are different engine sensors, and how do they work? >>