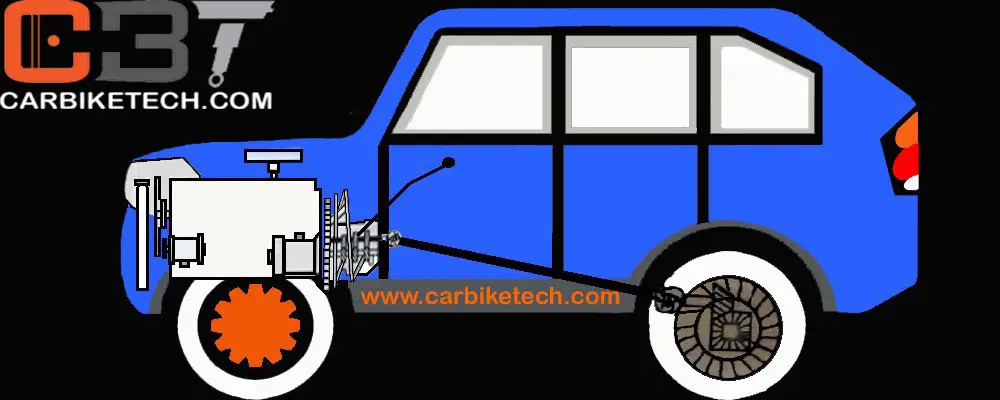
What is the Final Drive?
The Final Drive is the last gearing used while transmitting the engine power to the wheels. It has two purposes. Firstly, it turns the power flow from the propeller shaft to the rear axle at the right angle. Secondly, it also provides a mechanical advantage (leverage) from the propeller shaft to the rear axle. The Final drive contains a pair of spiral-bevel gears comprising a pinion that connects to the propeller shaft and a ring gear that connects to a flange on the differential case.

The pinion gets the drive from the engine while the crown wheel is attached to the wheels and rotates them. Usually, there are 3 to 4 times more teeth on the ring gear than the pinion. Thus, it provides the final speed reduction between 3:1 to 4:1. The drive pinion is an integral part of the pinion shaft. Its spline-end attaches to the end of the propeller shaft or the rear universal joint.
What is the Final Drive Ratio?
The final-drive ratio is the extent to which the rotating speed of the driveshaft (output) from the gearbox finally reduces before it reaches the driven wheels. If you alter this ratio, it also changes every gear’s effective ratio, affecting the vehicle’s performance and economy. Hence, the manufacturers term it as the final drive ratio. Basically, it is the final ratio of the gear train.

The gear’s angular velocity ratio gives the input to output ratio. You can easily calculate the final drive ratio directly from the number of teeth on the crown wheel and pinion. The manufacturers define the final drive ratio and mechanical ratio in such a way that it results in a number that forms an ideal association.
How does it work in a vehicle?
Let’s refer to the diagram above. E.g., there are 8 teeth on the pinion and 30 teeth on the crown wheel, as shown in the diagram. To rotate the crown-wheel (& thereby the wheels) by one rotation, the pinion needs to turn 3.75 times more. Let’s assume that the vehicle is traveling in the 4th gear whose gear-ratio is 1:1, which means the gearbox input is equal to its output.
In the 4th gear, the engine needs to turn the pinion 3.75 times more to rotate the wheels by one rotation. Thus, it means the engine itself needs to rotate 3.75 rotations to rotate the wheels by one rotation. Because
1 wheel rotation = 3.75 pinion rotations x 1 (1:1 ratio of the 4th gear in this case)
Therefore, 1 wheel rotation = 3.75 engine rotations (in 4th gear)
Caculation:
Thus, the engine turns 3.75 times to turn the wheels by one rotation in this case. Thus, the final drive ratio always reduces the engine speed to rotate the wheels by one turn. Similarly, in the 1st gear, whose ratio is 3.78, the engine must rotate 3.78 x 3.75 times more to turn the wheels by one rotation. Hence, this ratio is known as the final drive ratio.
1 wheel rotation = 3.75 pinion rotations x 3.78 (3.78:1 ratio of the 1st gear in this case)
Therefore, 1 wheel rotation = 14.175 engine rotations (in 1st gear)
That’s why the vehicles can climb the slopes easily in the first gear than other gears.
Need of the Final Drive in an automobile:
Generally, the Automobile drive train has two or more zones where the manufacturers use the gearing. One is in the gearbox, while the other is in the axle. Thus, it helps to deliver a great combination of the vehicle speed and torque at the wheels. Besides, the modern-day transmissions also employ the built-in differential gearing system. The manufacturers name such units as ‘Transaxle.’ The transaxle contains numerous different sets of gears that serve the purpose. It also includes the Final-Drive that provides further speed reduction at the wheels.
What is a ‘Transaxle’?
A transaxle is a combination of the transmission, and final drive (axle) merged into a single unit. Or else, these could be two separate units that connect thru’ a driveshaft. The gear ratios in the transmission and the final drive are vital. It is because they change the characteristics of the vehicle’s performance.
Furthermore, the differential contains a mechanism that splits the torque equally between the two wheels. It also allows them to rotate at different speeds while moving along a curved path. In most modern cars, the manufacturers employ the transaxle unit to reduce the weight or accommodate the Final-Drive in narrower spaces. Dana, Eaton, and Divgi-Warner are some of the leading suppliers of the final drive.
Read More: What is Rear Wheel Drive?>>