What Is An Oxygen Sensor?
Technically, oxygen is vital for an engine. It determines the proper engine performance. So, to achieve the correct air-fuel ratio, manufacturers employ oxygen sensors in the exhaust systems. Besides, the exhaust gas oxygen sensor is also known as the ‘lambda sensor.’ Its location is before the catalytic converter in the exhaust pipe. The sensor generates a voltage with regard to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. Thus, it provides real-time feedback on the mixture composition to the engine management system.

Furthermore, manufacturers calibrate the engine management system (EMS). As a result, it provides optimal engine power, emissions, and economy over the entire engine operating range. The oxygen sensor helps the EMS monitor the exhaust system’s optimum emission. Thus, it achieves the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7:1.
Design:
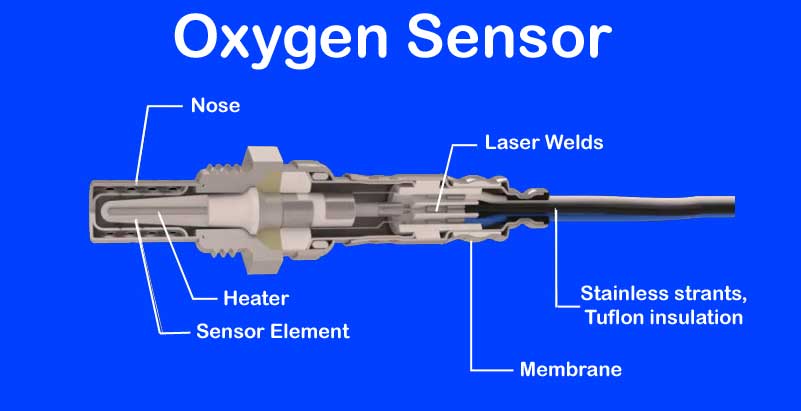
Furthermore, the oxygen sensor consists of a ‘galvanic cell’ battery. The sensor contains two porous platinum electrodes. Besides, they have a ceramic electrolyte (Zirconium Dioxide) between them. The oxygen sensor generates a voltage that ranges from as little as 100mV (0.1 volts) to a maximum of 900mV (0.9 volts). However, it depends upon the oxygen level in the exhaust gases. Besides, the oxygen sensor compares atmospheric oxygen, typically 21% approx., to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
Typically, a rich mixture contains more fuel per part of oxygen. Thus, it means that it has 0% oxygen. So, the sensor produces a high voltage of around 900mV. On the other hand, a lean mixture has less fuel per part of oxygen. It may contain 3% to 4% of oxygen. So, the sensor produces a low voltage of 100 mV. However, the average voltage of the sensor is ~ 450mV which results in the ideal mixture ratio of 14.7:1.
Criteria:
Rich Mixture – the significant difference between atmospheric and exhaust oxygen levels. It results in high conductivity between the electrodes. Hence, the voltage output is high at around 900mV.
Lean Mixture – the minor difference between oxygen levels. It results in less conductivity and smaller voltage output, typically around 100 mV.
Normal Mixture – when the mixture level is approximately 14.7:1. Then, the output from the oxygen sensor will be around 450mV.
Oxygen Sensor’s Features:
- It has a stainless steel wire. As a result, it provides better resistance to corrosion and thermal stress.
- Manufacturers use gold-plated terminals on signal and reference connector pins. Additionally, it gives superior contact for even minute voltage/current signals.
- A double laser-welded sensor body avoids moisture ingress to the sensor element/heater.
- Manufacturers conduct the functional quality test on O2 sensors at 1000°C.
- Manufacturers also test the ceramic thimble pressure at 420 bars to ensure integrity.
- Oxygen sensor measuring element undergoes “gas permeation” testing during manufacturing.

O2 Sensor Function:
Furthermore, oxygen is essential for the human body. Similarly, running the engine is also crucial and getting better performance. The oxygen sensor helps maintain the “Ideal” air/fuel ratio of 14.7:1 or Lambda 1. It provides a lambda value of 1 throughout various engine operating conditions. Besides, it compares the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas against the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere. With these differing amounts of oxygen, the oxygen sensor produces & sends a voltage output to the engine’s fuel management system.
Furthermore, AC Delco, Bosch, Denso, and Hitachi are some of the world’s leading manufacturers of O2 sensors.
Note: Images (courtesy: respective manufacturers)
Watch the Oxygen Sensor in action:
Read more: How do engine sensors work?>>