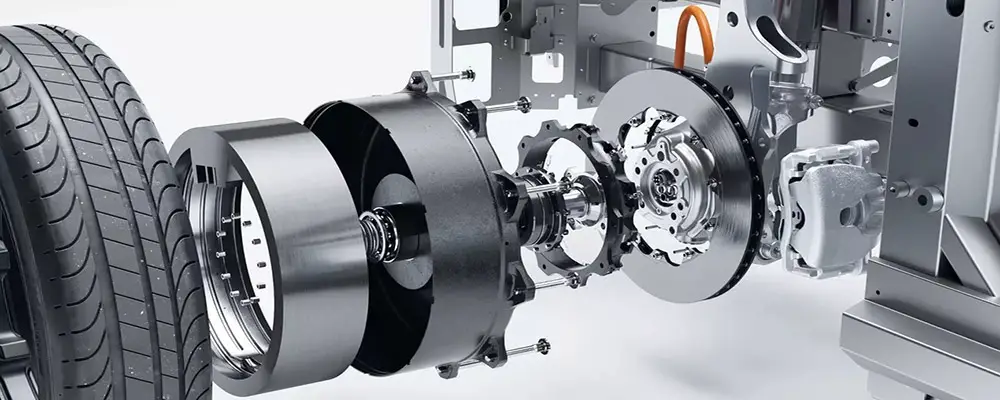
What is in wheel motor in EVs?
The in wheel motor is the placement of electric motors directly in the wheels. As a result, the drive is more pleasurable and intuitive because the motors are in close proximity to the wheels.
In addition, the driver gets more responses to its inputs delivering a fun experience. It is like driving an electric vehicle as you want it more responsively. This technology delivers a powerful driving experience as motors are in very close proximity to the wheels. This specific layout delivers greater control, flexibility, and freedom to the driver.
Technology Overview
The in wheel motor technology is a type of driving system in electric vehicles. The conventional EV designs have the placement of electric motors in the place of traditional IC engines. So, the gasoline engine is substituted by eclectic motors.
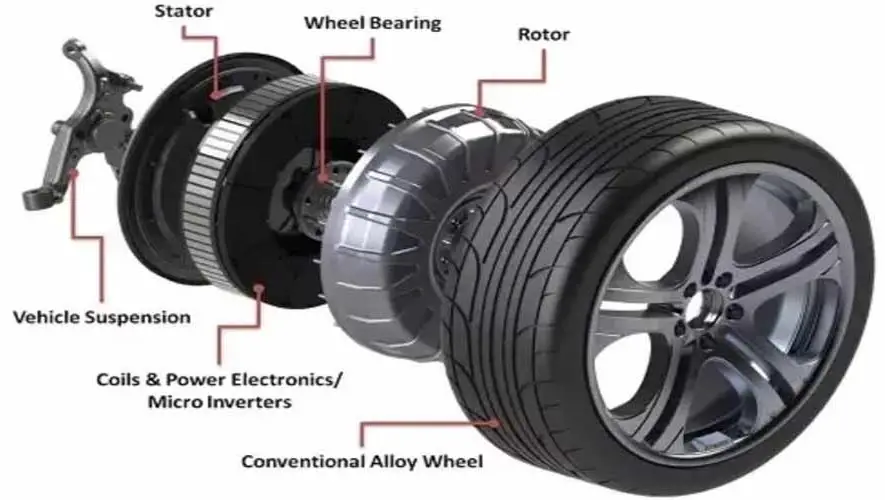
Furthermore, in the case of in wheel motor EV, the electric motor has direct placement inside each individual wheel. Therefore, EVs are very responsive to acceleration. In the case of this technology, we can fine-tune the responsiveness of each wheel.
In addition, the in wheel electric motors also improve steering response drastically. This is because these motors can independently control the left and right wheels. Hence, car behavior is more in line with steering. As a result, the driver can accelerate and corner intuitively as per his/her wish.
How in wheel motor technology works?
The traditional EV models place the electric motor directly in the place of the IC engine. Then the electric motor transfers the power to the wheels by a drive shaft. This particular method is helpful for auto manufacturers as it utilizes existing technology with the added benefit of minimal sound and vibrations.
Furthermore, the conventional setup transfers the power from the electric motor to the long drive shaft, ultimately transferring power to the wheels. So, the motor rotates the drive shaft, and the drive shaft then rotates the wheels. This entire process has a time lag, reducing the vehicle’s responsiveness.
In wheel motor, however, reduce this time lag. These motors have direct placement in the wheels and involve a small drive shaft to transmit power.
The small drive shaft has a little time lag resulting in instantaneous power delivery. This feature opens up the possibility of controlling the wheels precisely.
In addition, the in wheel motor drives each wheel independently. So, you can control the torque of the left and right wheels independently. So, for example, if the driver turns right, you can control the left-hand torque greater than the right-hand torque in accordance with how much the driver is steering the wheel.
The in wheel motor controls the reduction and increase in torque. As a result, you get a broader range of control, providing dynamic driving independence.
Image courtesy: Elaphe