Engine Design & Classification:
An engine is a power generating machine. It converts the potential energy of the fuel into heat energy and then into rotary motion. An automotive engine that produces power also runs on its own power. Overall, the manufacturers classify the engines according to their varied designs, constructions, and applications. Generally, automotive applications have the following sub-categories, by which; different engine designs vary from one another.
Automotive Engines are generally classified according to following different categories:
- Internal combustion (IC) and External Combustion (EC)
- Type of fuel: Petrol, Diesel, Gas, Bio / Alternative Fuels
- Number of strokes – Two stroke Petrol, Two-Stroke Diesel, Four Stroke Petrol / Four Stroke Diesel
- Type of ignition such as Spark Ignition, Compression Ignition
- Number of Cylinders – From 1 to up to 18 cylinders (in a car)
- Arrangement of cylinders which are Inline, V, W, Horizontal, Radial
- The motion of Pistons – Reciprocatory, Rotary
- Size / Capacity
- Bore-to-Stroke Ratio
- Engine cooling methods such as Air-cooled, Liquid-cooled (Water-based), Oil-cooled (Oil is cooled separately)
- Breathing such as Naturally Aspirated, Turbocharged / Supercharged
- Applications such as Bikes, Passenger Cars, Racing cars, Commercial Vehicles, Marine, Agricultural equipment, and Earth-moving equipment, etc.
The conventional automotive engine consists of the following parts:
- Engine Cylinder Head – Houses camshaft (in case of OHC design), inlet valves, exhaust valves, inlet manifold with turbocharger (if fitted), exhaust manifold
- Engine Cylinder Block – Houses main engine parts such as pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, oil pump, oil filter, oil cooler, water pump, and oil pan
- Alternator, A/c compressor, Power Steering Pump
- Flywheel, Clutch assembly, Clutch housing, Transmission
According to the arrangement of cylinders, an engine is classified primarily into the following categories:
- Inline
- ‘V’ shaped
- ‘W’ shaped
- Flat / Horizontally opposed
- Opposed Pistons
- Radial
However, the most commonly used engines in automotive applications are Inline, V, W, and Flat engine designs.
InLine Engine:
This type of design is a very basic and conventional engine design. In this engine construction, the cylinders are in a single straight line. An inline engine is used with 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or up to 8 cylinders. Read More.
‘V’ Engine:
This is a newer generation engine design. In this engine construction, the cylinders are at an angle. The angle between the cylinders form a ‘V’ shape and that is why it is a ‘V’ engine design. Read More.
‘W’ Engine:
In this engine construction, the engine has three rows of cylinders placed at an angle. The angle between the cylinder rows form a ‘W’ shape and that is why it is a ‘W’ engine design.

Typically, it is used in high-speed racing cars. The cars with 18 cylinders are some of Bugatti show cars – EB118 concept, EB 218 concept, 18/3 Chiron concept – all with an 18-cylinder ‘W-18’ engine and EB 18.4 Veyron Concept – with a 16-Cylinder ‘W-16’ engine.
Watch Bugatti Veyron W16 Engine Animation here:
Flat / Horizontally Opposed:
The main advantage of flat / horizontally opposed engines is that it allows a lower center of gravity, thereby helping in improving vehicle performance. This type of engine is used in Subaru cars.
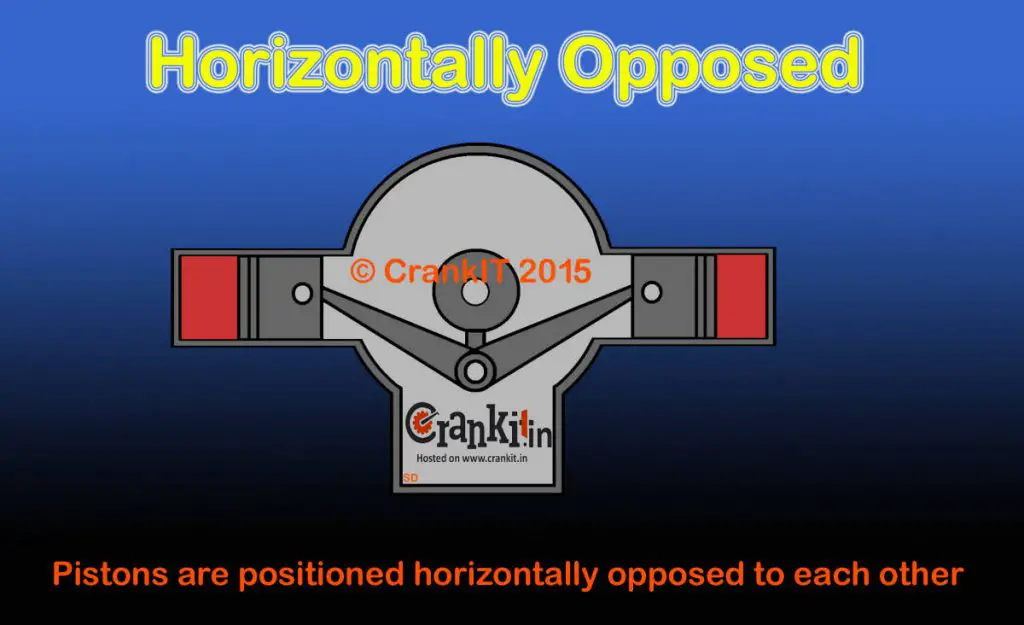
All Subaru models such as Impreza, Forester, Tribeca, Legacy, Outback, Baja, BRZ, and SVX use either a flat-four or flat-six engine.
Watch Flat Engine Animation Here:
For more information, please click:
Read on: What is engine capacity (CC)? >>
