What is an Automotive Clutch?
The meaning of clutch is to hold on to or grab or grip something. The automotive clutch is a device that engages and disengages the drive between two moving mechanisms or assemblies, such as a gearbox. One of them consists of the driving gears while the other has driven gears.
However, the driving gears get the engine’s rotating motion while the driven gears rotate the wheels. An automotive clutch connects/disconnects the engine with the gearbox that spins at different speeds than the engine. It allows the smooth shifting of gears by disengaging and re-engaging the engine from the gearbox when the vehicle is in motion.
Function:
The clutch ‘engages’ when it connects the two rotating shafts to lock together. Thus, they become one unit and spin at the same speed. It ‘disengages’ when the shafts are unlocked (not locked) and spin at different speeds. However, the clutch is said to be ‘slipping’ when the shafts are still locked together, but they rotate at different speeds.
In other words, the automotive clutch engages and disengages the power transmission to the gearbox while shifting the gears either accelerates or slows down the vehicle. Thus, it avoids the friction between the driving and driven gears being engaged/disengaged. It also prevents any damage to the gears. Generally, vehicles with manual gearboxes have a single clutch. However, automatic transmission vehicles could have more than one clutch.
Characteristics of automotive clutch:
The automotive clutch must possess the following qualities:
- Transmission of torque – It should be capable of transmitting the maximum engine torque.
- Gradual engagement – It should engage/disengage gradually and positively without any jerks/shocks.
- Dissipation of heat – Operation of clutch generates a large amount of heat. Hence, the clutch should ensure sufficient heat dissipation.
- Dynamically balanced – It must be dynamically balanced, especially in high-speed vehicles.
- Damping of vibrations – It must have a suitable mechanism for damping the vibrations and eliminating noise during transmission.
- Compact size – It must be of the smallest size and occupy a minimum amount of space.
- Free pedal play – It must have provision for the pedal play to reduce the effective clamping load on the thrust bearing and also its wear & tear.
- Ease of operation – It must offer an effortless/smooth operation of engagement/disengagement for the driver.
Components:
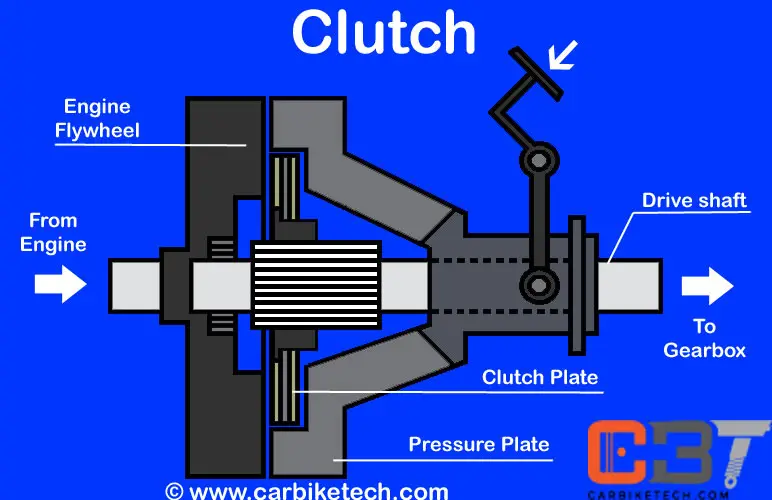
Typically, the basic clutch mechanism consists of a driven plate (or clutch plate), which has a splined hub at the center. It slides onto the gearbox’s driveshaft and presses against the engine’s flywheel. The clutch pedal performs the clutch operation with the help of a set of levers. First, it releases the driven plate, which gets pushed away from the flywheel. It occurs when the engine connects to the wheels. On the other hand, the pressure plate presses the driven plate against the flywheel. It consists of either several coil springs or a cone-shaped single diaphragm spring.

Types of automotive clutch:
There are different types of clutches depending upon their application. However, the manufacturers use the following types in the automotive drive transmission:
- Friction – Most common type and basic clutch. It uses friction to synchronize the speeds and/or to transmit power.
- Mechanically operated – Operates using mechanical linkages, typically used in old trucks. However, it needs more force to operate.
- Hydraulically operated – Operates using hydraulic cylinders, typically used in cars. Thus, very light to operate.
- Dry-type – This is the most common type of automotive clutch which most vehicles employ. The dry clutch system uses only friction to engage.
- Wet type – This clutch is immersed in the lubricating oil, typically used in motorcycles.
- Pull type – The pressing of the pedal pulls the release bearing, pulls the diaphragm spring, and disengages the drive.
- Push type – The pedal pressing pushes the thrust bearing on the clutch and disengages the drive.
- Single plate – Uses only one friction plate.
- Dual-clutch – It uses two separate clutches – one for odd and the other for even gears.
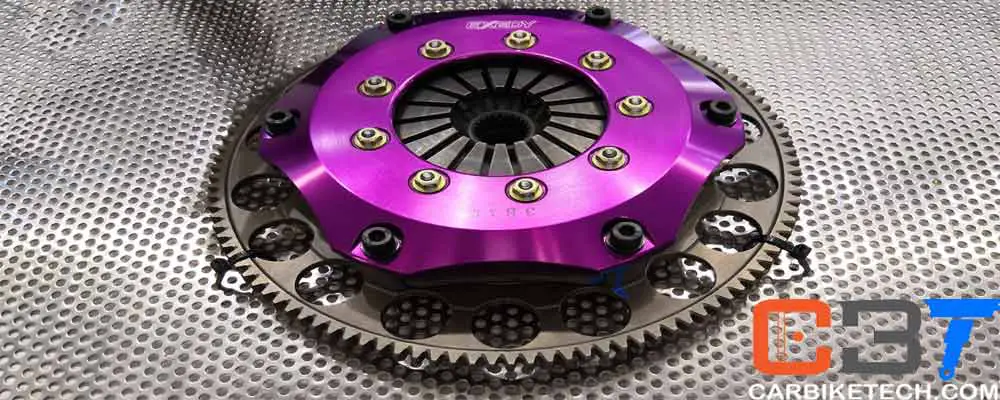
- Multi-plate – Uses multiple friction plates.
- Slipper clutch – Used to eliminate the effects of engine braking.
- Overrunning clutch – It automatically disengages if the driven member rotates faster than the driving member.
- Lock-up clutch – Above a certain speed, it locks up the torque converter. This minimizes the power loss and improves fuel efficiency.

Dual dry clutch (Courtesy: Valeo)
Friction Clutch:
The best type of clutches is a friction clutch. Hence, vehicle manufacturers prefer this type of clutch on most vehicular applications. The manufacturers make clutches from a variety of materials, including asbestos. However, asbestos particles are harmful to human health, and hence, manufacturers later discontinued their use.
Nowadays, modern vehicles’ clutch employs organic compound resin with a ceramic material or copper wire. However, heavy commercial vehicles still use only ceramic lining/material for the clutch. The friction clutch is of two types. They are the push type or pull-type one. However, it depends upon how the pressure plate lifts from the fulcrum points. Eaton, Valeo, and Ceekay Daikin are some of the manufacturers of automotive clutches.
Application of multi-plate automotive clutch:
The motorcycles and high-speed cars use the multi-plate clutch system to transmit the torque. This design comprises many driving plates “stacked” onto several driven plates. Racing cars such as the Formula 1, World Rally Championship, and most club-racing cars use the multi-plate clutch. The drag-racing cars which need lots of acceleration also use the multi-plate clutch. However, it results in the clutch getting a lot of abuse.
Note – Title Image : Courtesy: Eaton
