Tyre: Classification and Nomenclature
A tyre (or tire) is a circular and ring-like part of a vehicle that comes in contact with the ground. Tyres are fitted on rims and filled with compressed air. Since their invention, natural rubber has been the most widely used material in the manufacturing of tyres. However, modern tyres also employ materials like synthetic rubber, fabric, steel wires, carbon black, and some more compounds. As a result, tyres find a place in a wide range of locomotives, from bicycles to aeroplanes.
Classification of tyres:
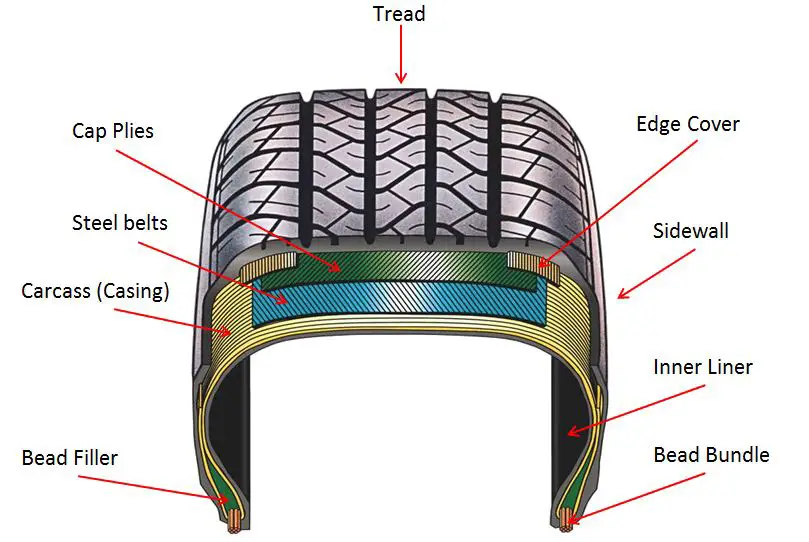
In general, there are two major classes of tyres, according to the presence or absence of tubes in them. Thus, they are called ‘tubed tyres’ and ‘tubeless tyres,’ respectively. Furthermore, based on the construction or skeleton of tyres known as carcass, tyres are classified into the following main types:
1. Cross-ply or bias-ply: In these tyres, ply cords are at an angle of 30°-40° to the tire axis.
2. Radial ply: Ply cords run in the radial direction in these tires.
3. Belted-bias ply: This is a combination of the aforementioned types.
However, most of the tyres used nowadays belong to the class of radial tubeless tyres.
Functions of a tyre:
1. To maintain contact between vehicle and ground by providing the desired traction.
2. To support the load of the vehicle.
3. Dealing with various forces acting on the vehicle during its motion.
4. Providing cushions against shocks and damping them.
How to read tyre nomenclature?
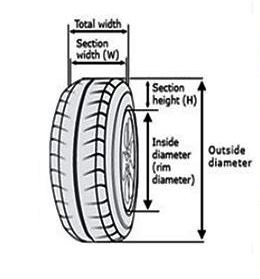
There is a specific method of denoting the size of tyres. Manufacturers often call it the ‘tyre-nomenclature’ or ‘tyre-code’ and mark it on the sidewall of tyre. Every term of this specification has some meaning associated with it. Selecting a proper tyre for a vehicle would be impossible unless one understands these terms perfectly. A typical tyre nomenclature of a passenger car tyre is as below:
175/65 R 14
In the specification mentioned above,
175: Nominal section width in mm
65: Aspect ratio. It means the section height of the tire is that many percent of its section width, i.e., 65 % of 175 =114 mm(Approx.)
R: Denotes the construction of the tire, which is Radial in this case
14: Rim code or rim diameter in inches
In addition, some manufacturers also specify the speed and load rating of tyres in the nomenclature. Based on these parameters, one can determine the maximum speed and load that a tire can withstand. Buyers can easily decode these terms from the manufacturer’s catalog or the charts available in any standard reference manual. In recent period lots of futuristic tyres have been designed, here is one of them by Goodyear called Goodyear eagle 360
Bridgestone, Goodyear, Pirelli, MRF, and Apollo are some of the famous tyre manufacturers in the world.
