Naturally Aspirated Engine (NA): Design And Characteristics
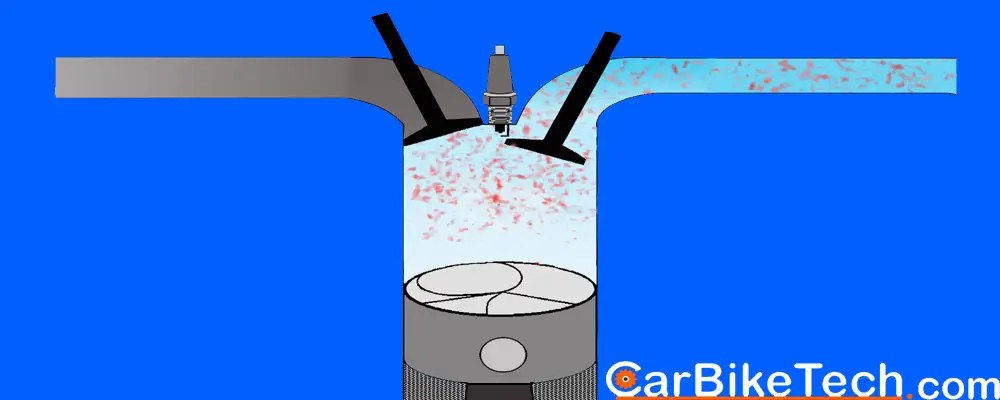
The term NA stands for the Naturally Aspirated engine. This term applies only to an internal combustion (IC) engine. In an IC engine, the intake of the air completely depends upon the atmospheric pressure. So, manufacturers term it as naturally aspirated or naturally breathing.
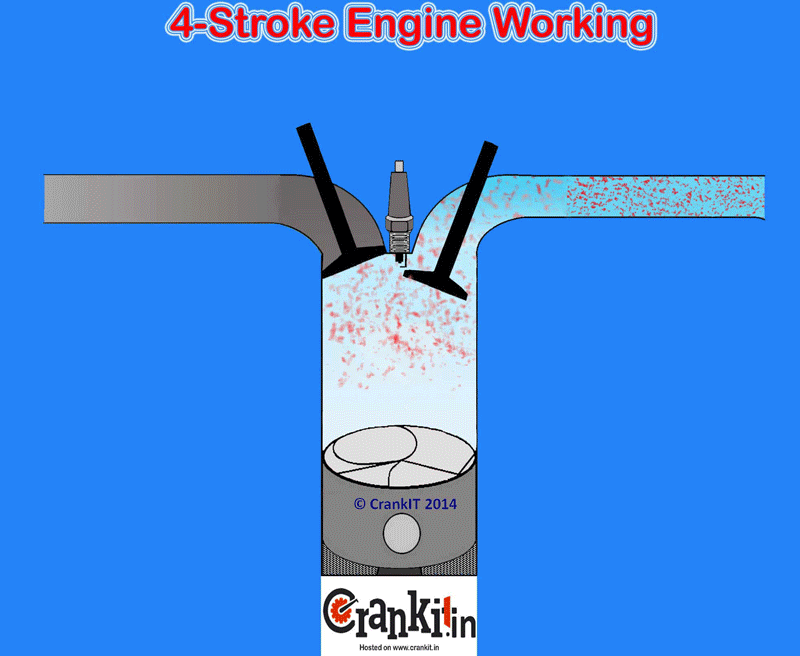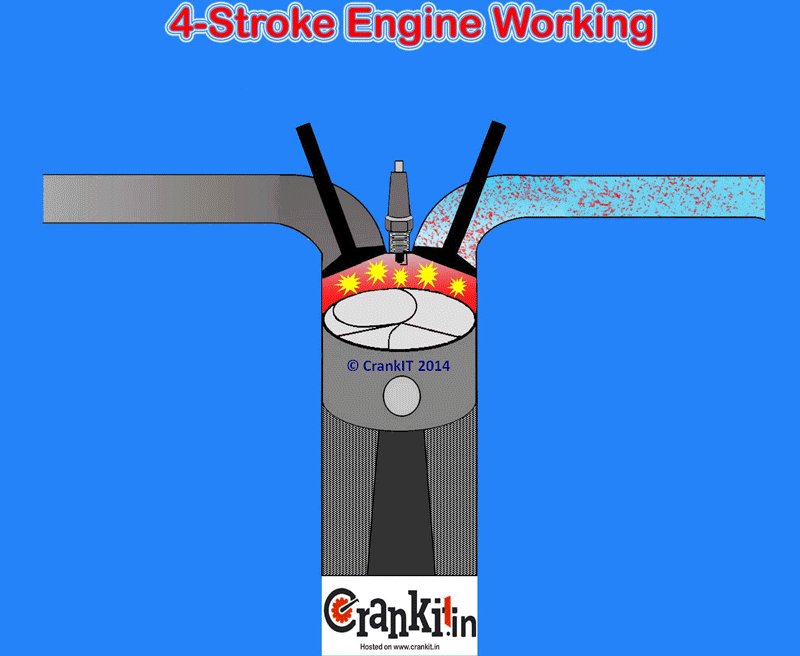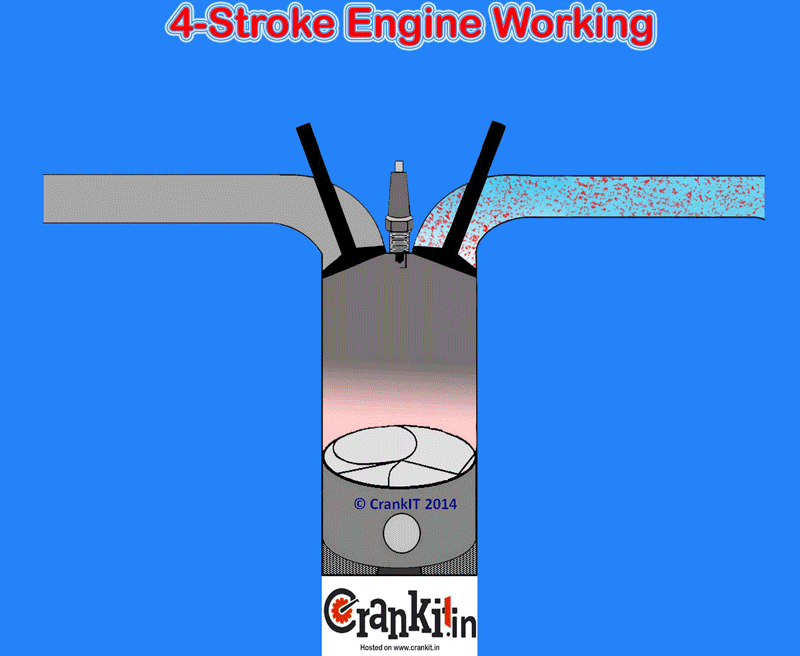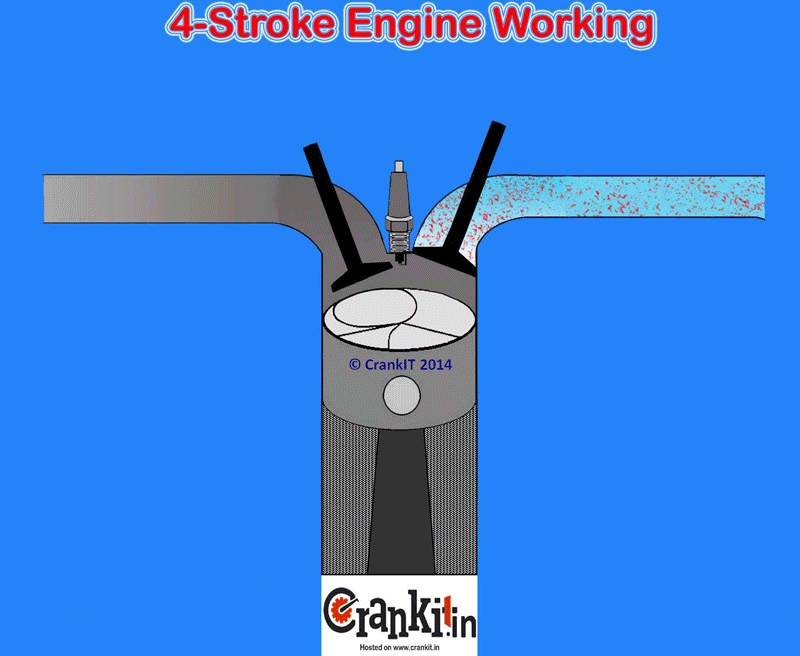
When the engine inlet valves open, they fill the cylinder with a fresh air or air-fuel mixture (charge). The engine cylinder sucks the charge (or just the air in case of diesel and gasoline direct injection engines) because of the atmospheric pressure and the vacuum created by the descending piston. It DOES NOT use an external mechanism to force the air into the cylinders. Hence, the manufacturers term this type of engine as naturally aspirated.
Naturally Aspirated Engine vs Turbocharged Engine:
The naturally aspirated motor uses only atmospheric pressure and vacuum in the inlets to fill the cylinders. This engine differs from the force-fed engine which uses blowers to force more air into the cylinder than it is naturally possible. Hence, supercharged and turbocharged engines do not count as the naturally aspirated type of engines.

The naturally aspirated engine draws the air for combustion into the engine cylinders only by atmospheric pressure. It acts against a partial vacuum which the piston creates when it travels down towards the bottom dead center. This happens during the intake stroke in naturally aspirated cylinders. Due to a natural restriction in the engine’s intake path which includes various inlets, a small drop in the pressure occurs as air draws in.
Consequently, a naturally aspirated engine gets less air-charge inside the cylinder. Thus, it delivers lower volumetric efficiency and a low mass-to-volume ratio of the air/charge. Therefore, it also affects the engine’s maximum theoretical power output. The atmospheric pressure decreases with the increase in the operating altitude. This loss of air is beside the losses due to the restrictions in the induction system.
Naturally Aspirated Engine applications:
Most automotive petrol engines and small engines made for non-automotive purposes use NA engine technology. Nowadays, many diesel engines which power commercial vehicles have a turbocharger. They produce a more useful power-to-weight ratio. These engines also give better fuel efficiency and lower tailpipe emissions.
Advantages of NA Engine:
- Less number of parts
- Low cost of manufacturing
- Simple and easy to produce
- Low cost of ownership
- Low cost of maintenance
- Great throttle response (No lag)
Disadvantages of NA Engine:
- Lower power-to-weight ratio
- Lower efficiency
- Incomplete combustion resulting in the higher emission
For more information, please click here.
Watch the Naturally Aspirated engine in action here:
Read On: What is a 4-Valve engine?