EFi, MPFi, GDi –
EFi stands for Electronic Fuel injection (EFi) whereas MPFi or MPi stands for Multi-Point Fuel injection and GDi stands for Gasoline Direct Injection. All these are the types of fuel injection systems which the gasoline or petrol fuel engines mainly use. All these terms refer to the newer generation Petrol Injection systems.
Earlier, older engines used simple Fuel Injection (Fi) which replaced the carburetor to overcome some of its shortcomings. The carburetor, being a mechanical device, was just not fully capable of controlling an accurate air-fuel ratio to meet the growing demands for better emission control.
Hence, it was replaced with first generation Fuel Injection technology. In this method, the petrol fuel is atomized by forcing it thru’ an injector as opposed to its suction created in a venturi tube in a carburetor which lifts the petrol thru’ its orifices. Thus, there is a fundamental difference between the earlier generation carburetor & newer generation Fuel Injection (EFi) system.
Earlier, the first generation Fuel Injection featured a simple design which consisted of an injector and a mechanical fuel pump. Basically, the fuel pump provided sufficient pressure to open the injector hydro-mechanically. Later, this system was upgraded to include electrically operated Injector by an ECU which is the first generation Electronic Fuel Injection systems or EFi.
Throttle Body Injection (TBI) –
Throttle Body Injection is also known as Central Fuel injection system. It consists of an electrically controlled fuel injector placed above the butterfly valve (throttle) and sprays fuel into the throttle body.
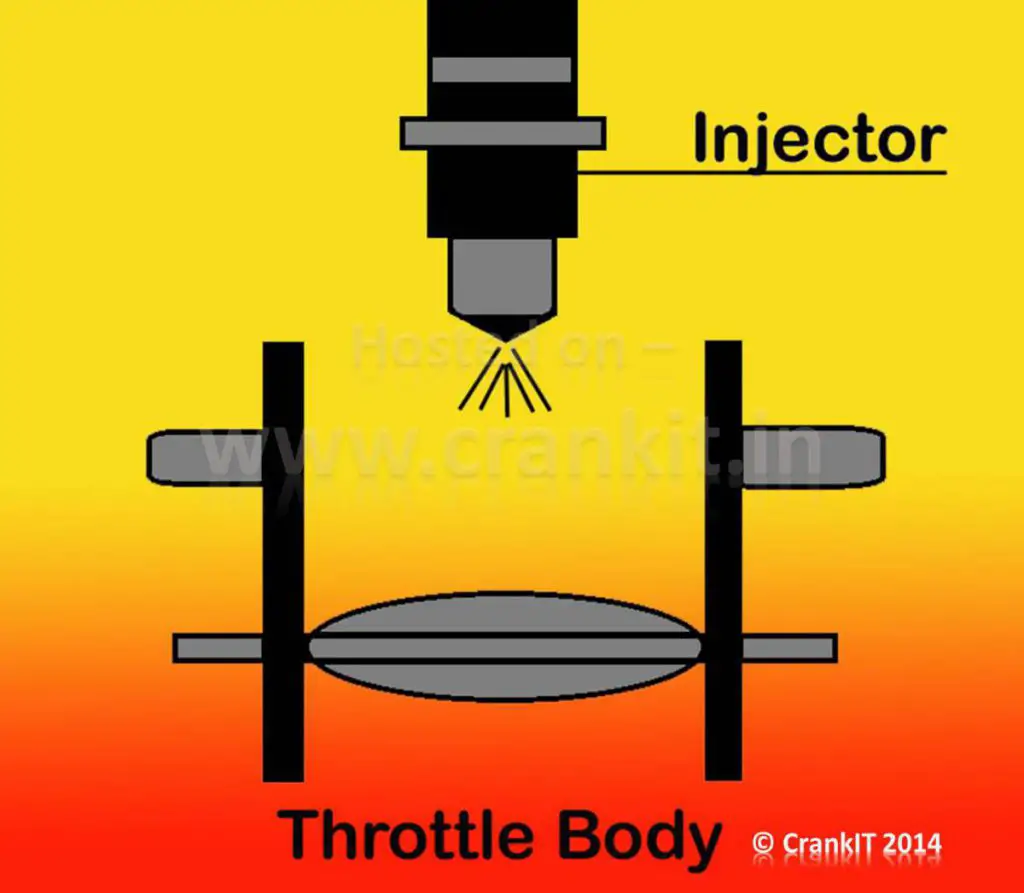
Single-Point Fuel Injection –
Single Point Fuel Injection is the second generation Fuel Injection system which used electronically controlled Fuel Injection (EFi). Furthermore, it governed the injection timing accurately with the help of an ECU, sensors, and actuators. It used a ‘common-to-all-cylinders’ injector which supplied petrol in atomized form.
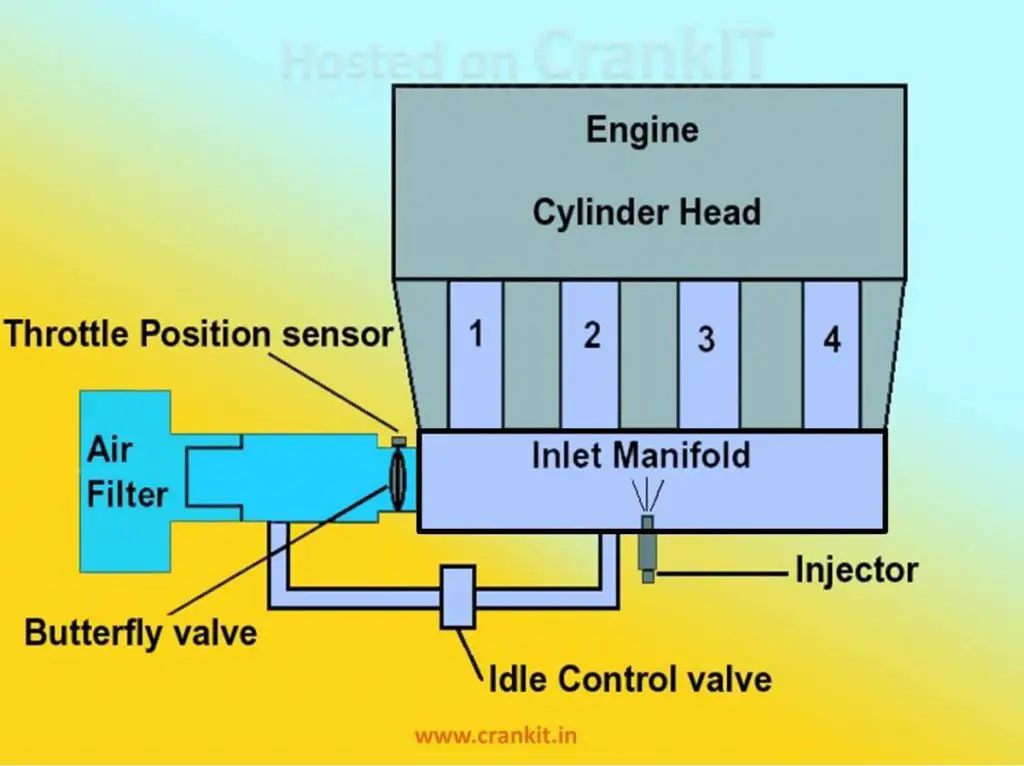
However, the engineers moved it from its earlier position in the throttle-body to the intake manifold. Here, the petrol mixes with the incoming air. Then, the air-fuel mixture (known as charge) goes to each cylinder. Hence, this system is also called the “Manifold Injection” since the injection of petrol occurs inside the inlet manifold.
Multi-Point Fuel Injection (MPFi) –
Furthermore, the manufacturers developed the Manifold injection system to include ‘one-for-each-cylinder’ injector which provided four injectors to in a four-cylinder engine. The engineers labeled this electronically controlled, superior technology as the ‘Sequential fuel injection’ aka Multi-Port / Multi-Point Fuel Injection or in short the MPFi / MPi.
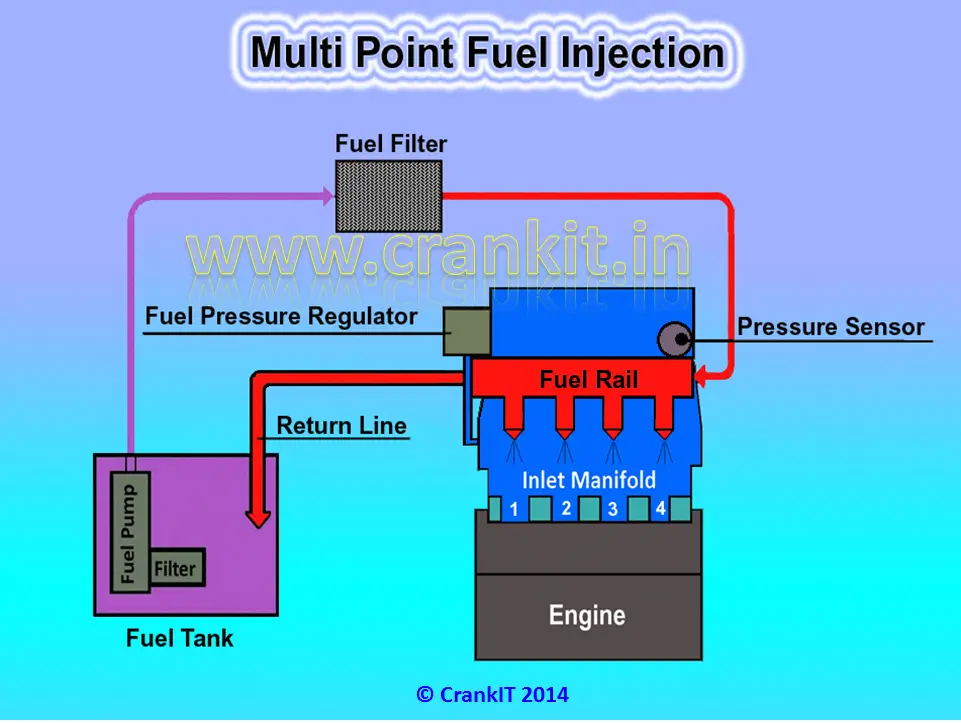
The MPFi uses separate injector for each cylinder to supply the correct quantity of fuel via a ‘fuel-rail’ according to the ‘Firing Order’ or in a ‘particular sequence’. Also, MPFi system provides further precision by varying the fuel quantity and injection timing by governing each injector separately. It thereby improves the performance and controls the emissions effectively.
This technology consists of the following parts:
1. Injectors
2. Fuel Pump
3. Fuel Rail
4. Fuel Pressure Sensor
5. Engine Control Unit
6. Fuel Pressure Regulator
7. Various Sensors – Crank/Cam Position Sensor, Manifold Pressure sensor, Oxygen Sensor
#Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) –
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) is also known as Petrol Direct Injection / Spark Ignited Direct Injection (SIDI) / Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) which is the latest EFi technology. Additionally, it uses special injectors that spray the petrol at a very high pressure. Unlike the MPFi system, this injector sprays the petrol directly into the combustion chamber just like diesel engines.
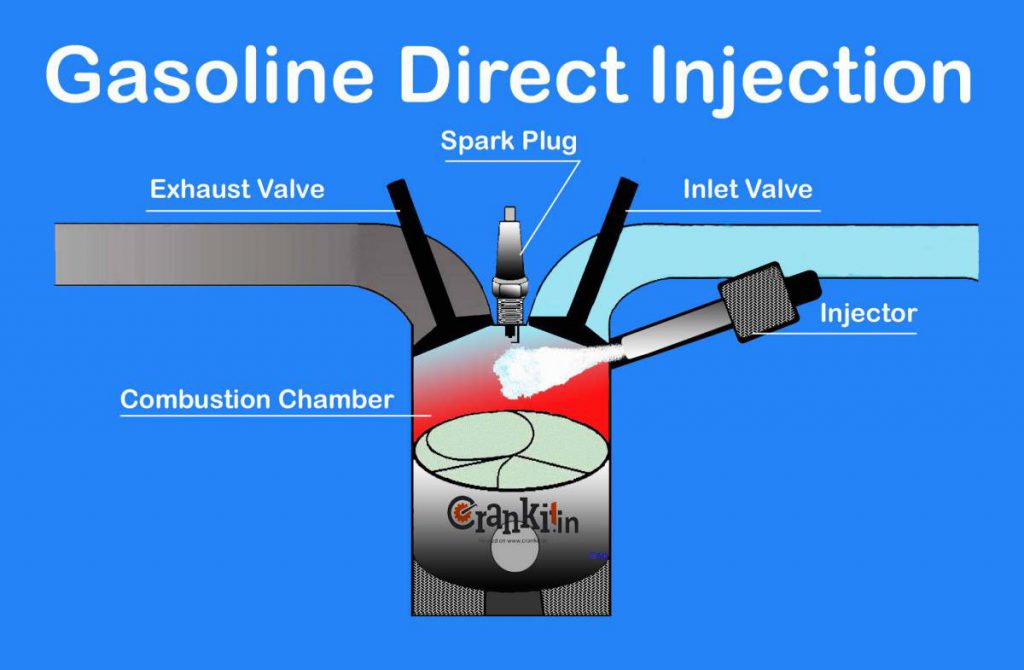
The sophisticated ‘Engine Management System’ (EMS) precisely controls the mixing of air & fuel. The mixing of air and petrol occurs inside the combustion chamber rather than in the inlet manifold. Thus, this method provides greater control over the combustion process. In addition, it also provides multiple combustion modes which include ultra-lean-burn air-fuel ratios. Nowadays, newer generation engines use GDI in combination with a Turbocharger which improves engine performance.
Benefits of Fuel Injection in Petrol Engines are –
1. Smoother and more reliable engine response
2. Elimination of the choke and easier cold starting
3. Better engine operation even at extreme ambient temperatures
4. Smoother engine idle and running
5. Increased fuel efficiency
6. Reduced CO2 emissions
For more information, please click here.
Read more: How CRDi technology works?>>
