Drum Brake Working Principle:
Two-wheelers such as scooters, commuter bikes, three-wheelers including auto-rickshaws widely use the Drum Brake system for braking. This type of brake system is used on the rear wheels of most hatchback cars, entry-level sedans & MUVs. It is also widely used on both front & rear wheels of trucks, buses, and other commercial vehicles in combination with hydraulic/pneumatic (either air-pressure or vacuum) brake actuating systems.

This system is also known as the ‘Internal Expanding Shoe Type’ brake system. This type of brake got its name from the drum structure of cylindrical-shape. Inside this drum, the parts of the conventional drum-brake system are housed. Hence, the name.
These parts include:
- A cylindrical drum itself made of cast iron
- A brake shoe actuating mechanism – either by a cam or a hydraulic wheel cylinder
- A pair of brake shoes (one each of Leading & Trailing)
- Shoe adjuster
- Return springs
- Anchor Plate / pins etc.
How does Drum Brake work?
There are mainly three types – mechanical, hydraulic & pneumatic assisted brakes.
1. Mechanical:
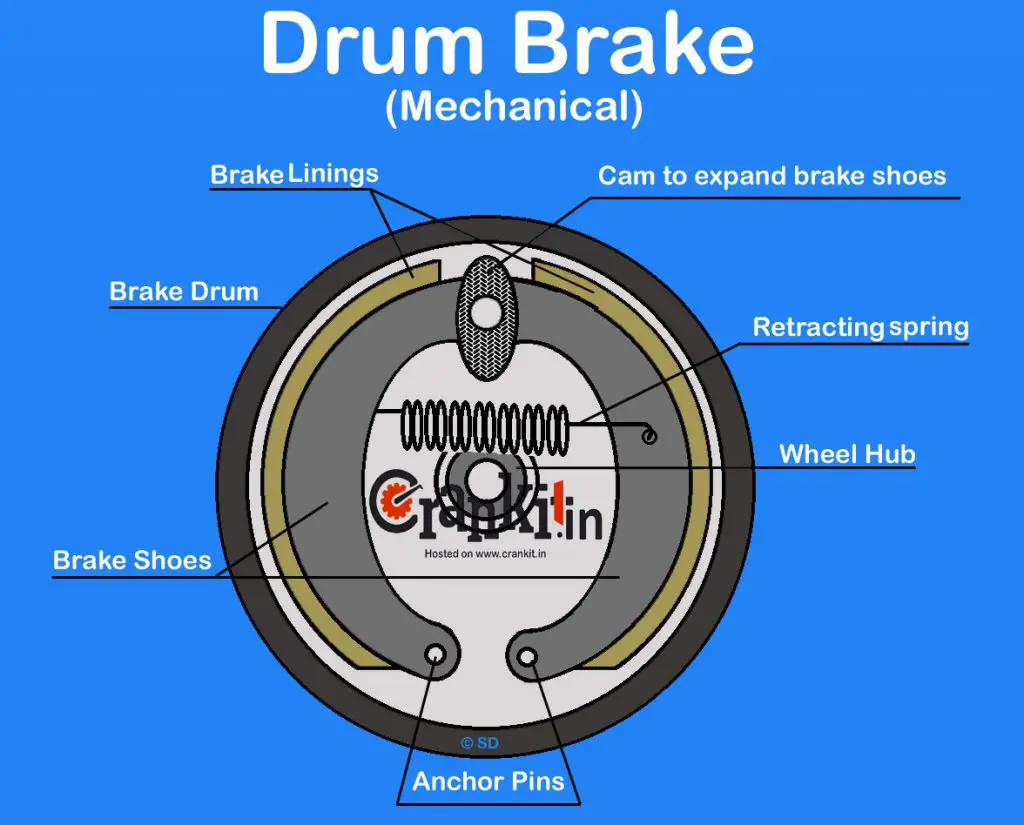
In the mechanical system such as in two-wheeler & an auto-rickshaw, the brake shoes are actuated by a cam, which is attached to the brake linkage & pedal. When you press the brake pedal, the cam turns. Thus, it causes the brake shoes to expand outwards and rub against the drum.
The friction between the brake linings and the drum causes the drum to stop rotating; thereby stopping the wheel. When you release the brake pedal, the retracting springs bring the brake shoes back to their original position. This results in a gap between them and the drum and to again spin it freely.
2. Hydraulic:
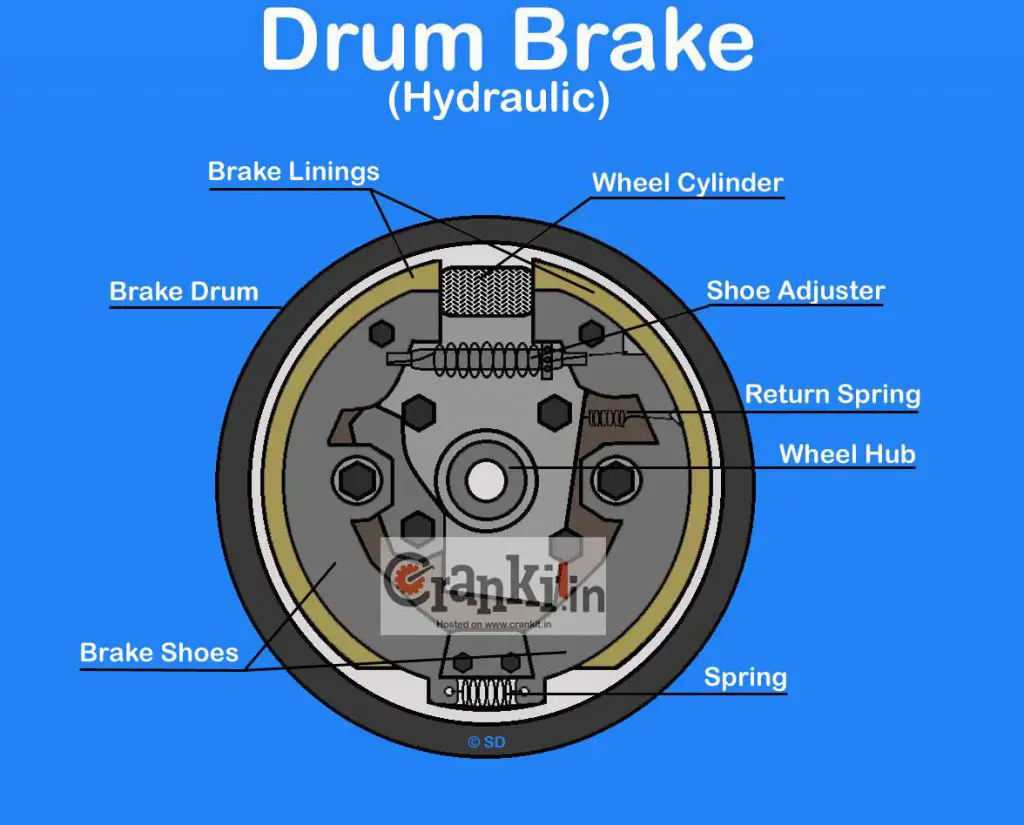
The hydraulic brake system such as in cars is a bit superior to the mechanical one. In this design, the hydraulic wheel cylinder replaces the cam. In the hydraulic system, instead of a cam, the wheel cylinder’s pistons push the brake shoes outwards.
The brake shoes fit on the anchor plate or braking plate. It holds the brakes system parts together and on to the car’s axle. When you press the brake pedal, the oil in the brake master cylinder multiplies the hydraulic force sent to the wheel cylinders. Thus, it causes its pistons to push outwards. The pistons, in turn, cause the brake shoes to expand and rub against the drum. The friction between the brake linings and the drum causes the drum to stop rotating, thereby the wheel to stop.
3. Pneumatic Assisted:
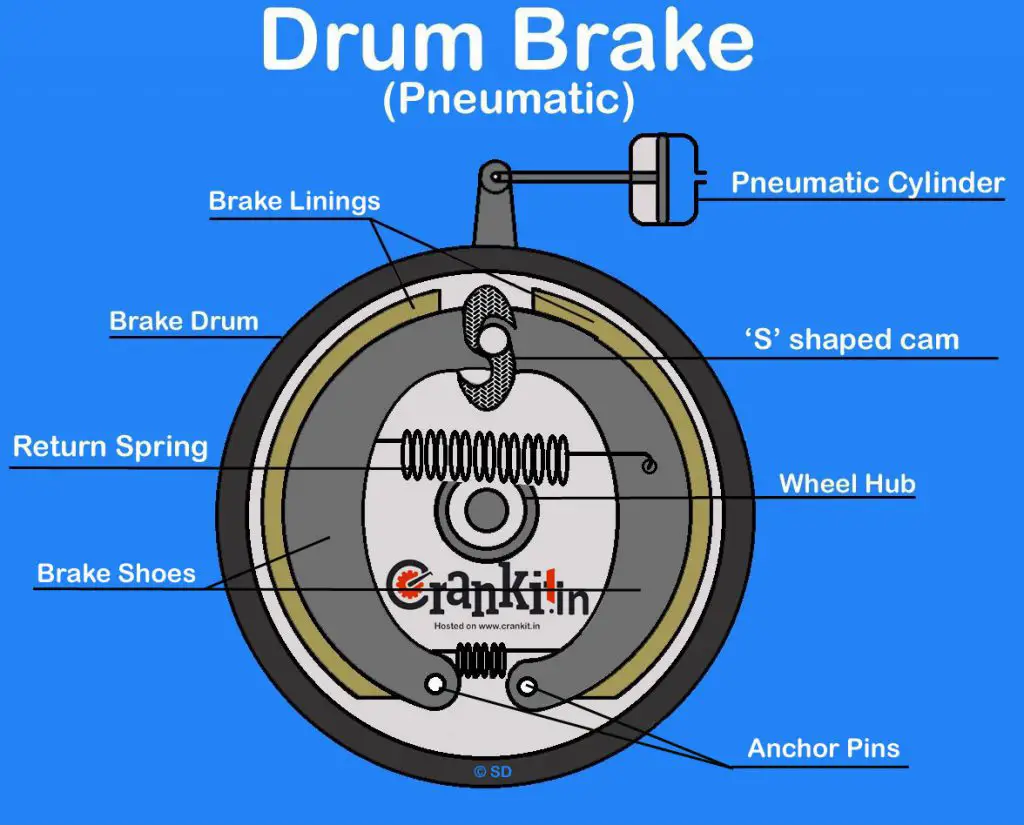
Furthermore, the third type is the pneumatic-assisted brake system. It is actuated by air-pressure which works on the same principle of that of the mechanical brake system. It also consists of a bigger size cam or the ‘S’ shaped cam. Another name for this brake is the “S-Cam” brake system. However, high-pressure compressed air actuates a pneumatic piston that turns the cam. Mostly the medium to heavy commercial vehicles use this type of brake system.
Advantages of Drum brake system:
- Simple design.
- Fewer parts.
- Easy & cheaper to manufacture.
- Low maintenance cost.
- Comparatively longer life.
Disadvantages:
- Low braking force compared to Discs.
- Brakes ‘fade’ when the driver applies them for a prolonged time.
- The brake shoe lining made of asbestos is harmful to humans.
- When wet, the braking grip reduces considerably.
- Non-asbestos linings catch moisture; causing the brakes to grab suddenly.
For more information, please click here.
Watch Drum Brake in action here:
Read More: How Disc Brakes work?>>
