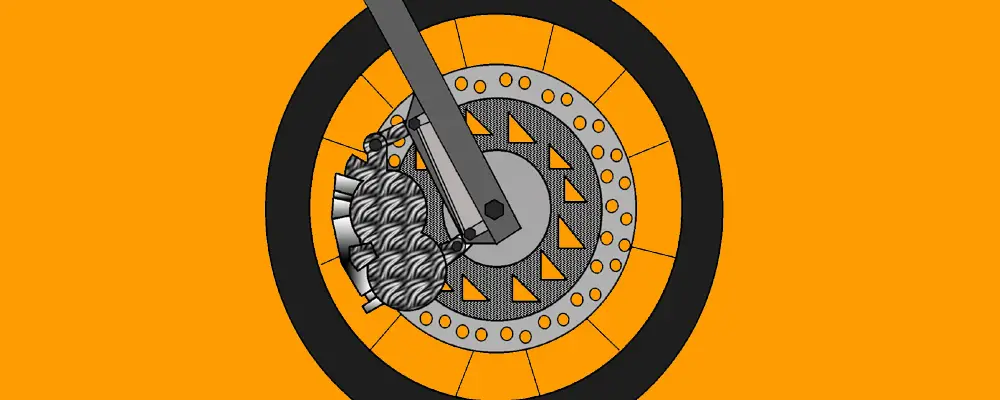
Disc Brake Working Principle:
Disc brake system is widely used on front wheels in mid-range two-wheeler such as – commuter & sports bikes. The Disc brake system is used on the front wheels of most hatchback cars, entry-level sedans & MUVs; whereas, it is also widely used on both front & rear wheels of high-end cars and SUVs in combination with hydraulic / vacuum brake actuating systems.
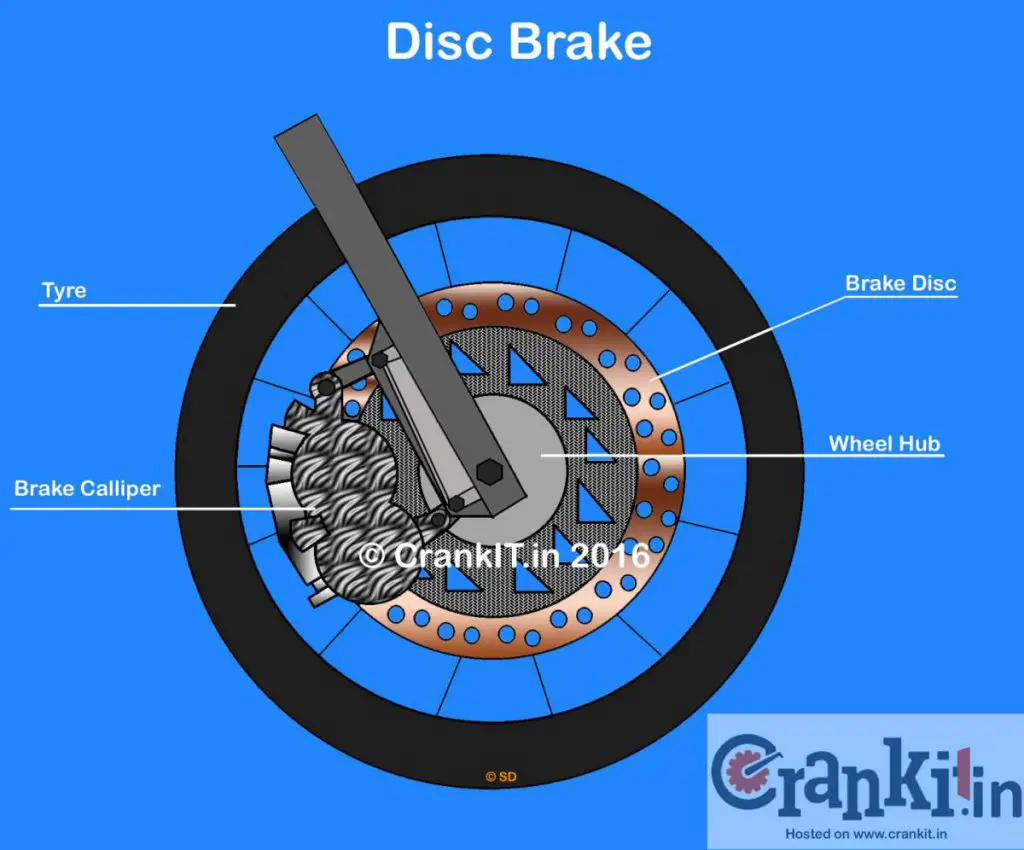
Disc brake got its name from the circular-shaped plate or disc or rotor; onto which the disc brake parts are mounted. A conventional Disc Brake system consists of a brake disc, two friction pads, and brake caliper. In the Disc brake system; the friction pads apply grip on the external surface of the disc to perform braking. The disc brake consists of:
- A circular disc made of – cast iron in cars and steel in two-wheeler
- A caliper assembly consisting of hydraulic pistons
- A pair of brake pads (one each on either side)
- Bleed screw
Following types of Disc brake systems; which are in use –
1.Single piston:
In the single piston design such as in two-wheelers, the brake pads are actuated by a single piston, which is attached to the brake caliper. When you press the brake lever, the brake oil pushes the piston causing the brake pads to contract and rub against the disc. The friction between the brake pads and the disc causes the disc to stop rotating, thereby the wheel to stop. When you release the brake lever, the brake pads retract to their original position. This causes a gap between them and the disc and to again spin it freely.
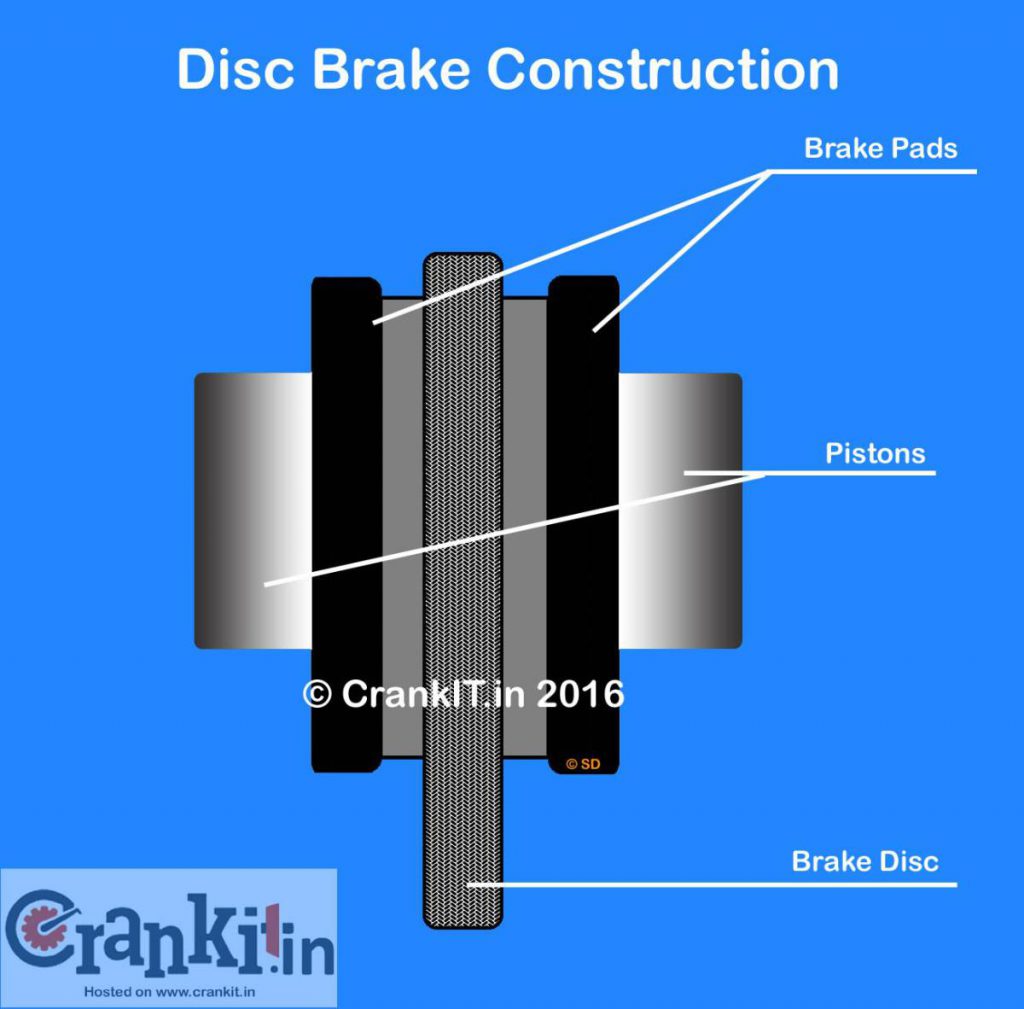
2.Twin Piston:
The twin piston design such as in cars is almost identical to single piston one, except for the pistons which are two in numbers. In this system, the twin pistons push the brake pads to apply the brake. The brake pads fit on the caliper which holds the brakes system parts together. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the oil in the brake master cylinder multiplies the hydraulic force sent to the calipers; causing its piston to contract. The pistons, in turn, cause the brake pads to contract and rub against the disc. The friction between the brake pads and the disc causes it to stop rotating, thereby the wheel to stop.
3.Twin caliper:
The third type – Twin caliper system; actuated by two callipers which works on the same principle of that of single caliper brake system. In this design, there are two calipers instead of one. However, the high-speed luxury cars more commonly employ this type of system. This system provides more effective braking.
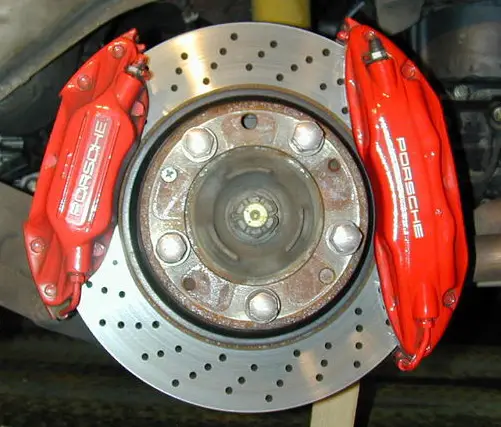

Ventilated Discs –
Modern vehicles come with ventilated discs. When you apply brakes, it converts the kinetic energy of the vehicle to heat due to the friction between the brake pads and the disc. Ventilated discs have passages or an air vent that helps pass air through the disc. Thus, it provides cooling & prevents brake fading.

Advantages of Disc brake system:
- No adjustment required. So, no maintenance.
- Better stopping performance
- Fade-free braking in all conditions. So, no fading of brakes.
- Can check wear without dismantling the unit
- Easy & quick to replacement of pads compared to Drum brakes

Disadvantages of Disc Brake system:
- High braking force needed compared to Drum brake
- Low life of brake pads compared to brake shoes
- Need separate hand-brake mechanism when fitted to rear wheels