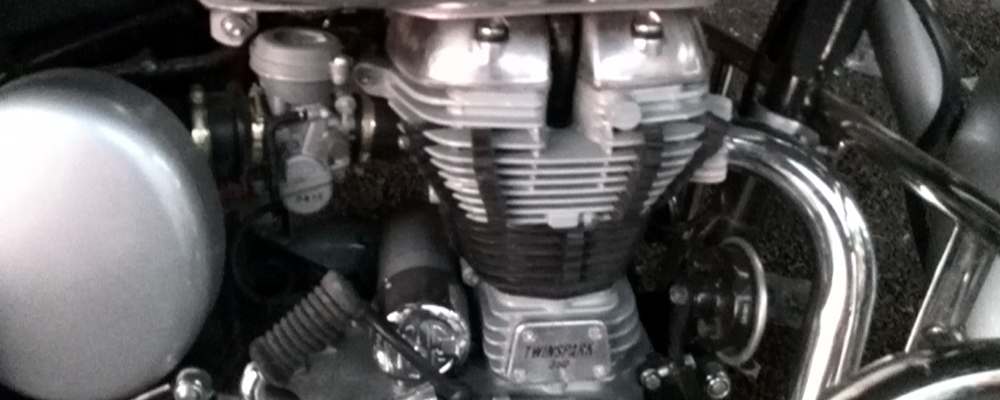
Air cooled engine design:
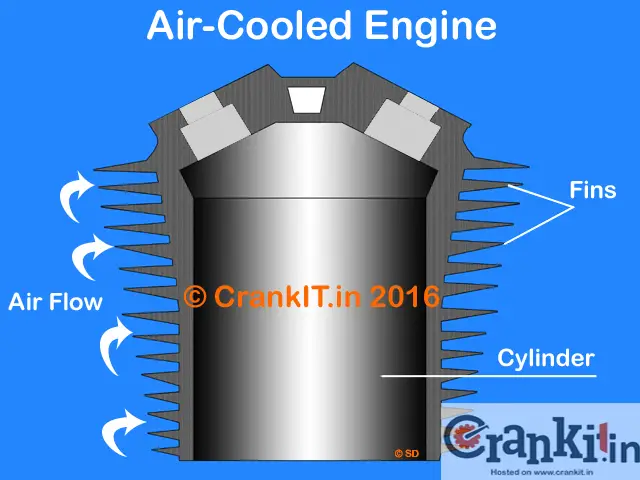
As the name suggests, if an engine is cooled only by the circulating air over its hot parts then it is known as an air cooled engine. An air-cooled engine has a simple design. It has metal fins on the outer surface of head and cylinder block which increase the area exposed to the cooling air. These fins provide a larger contact area so as to achieve better heat dissipation.
This is achieved by natural air flow due to the forward motion of the vehicle. It is typically used in entry-level two-wheelers such as scooters, bikes, small generators, and ATVs. In the large air-cooled engines of cars, cooling fans are used to direct the air on cylinder head & block. The air-cooled engines tend to have higher lube oil consumption due to the burning of oil in the combustion chamber.
The dissipation of the heat depends on the following factors:
- Surface area of the metal in contact with the air
- The rate of air-flow.
- The temperature difference between hot surface & the air.
- Heat conductivity of the metal used
Fins are provided on the cylinder head and block to increase the effective surface area of the metal coming in contact with air. More the surface area in contact with cool air diddipates more heat. Similarly, higher the rate of air-flow, higher is the dissipated heat.
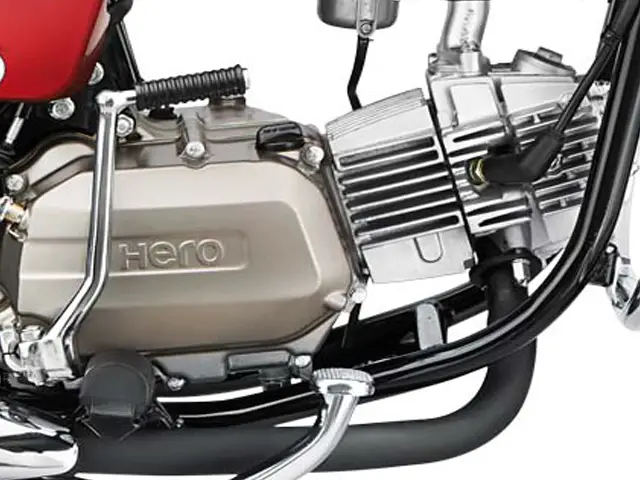

Advantages of an air-cooled engine:
- Simple design
- Easy & cheap to manufacture
- Lighter in weight due to the absence of radiator, cooling jackets & coolant.
- Does not need the topping up of coolant(anti-freeze)
- Suitable in cold climates where water may freeze.
- Less number of parts, lower maintenance
Disadvantages of an air-cooled engine:
- Not suitable for multi-cylinder engines without a fan
- No control on engine heat dissipation, hence less efficient
- Not very effective at high ambient temperatures
- It affects the engine efficiency because of variation in temperature due to varying speed
- Limited use such as in scooters & motorcycles
